What is a cryptocurrency transaction blockchain confirmation?
Last updated
Confirmations are a fundamental aspect of how blockchain and cryptocurrencies operate. They ensure that transactions are recorded properly on the ledger, maintain the security of the network, and help prevent fraud. When sending or receiving cryptocurrencies, it’s important to remember that transactions aren’t considered finalized until there are multiple confirmations.

Table of Contents
The Basics of Blockchain Transactions
A blockchain, the technology that underpins cryptocurrencies like Bitcoin and Ethereum, is essentially a decentralized ledger of all transactions across a peer-to-peer network. Whenever a cryptocurrency transaction occurs, it needs to be added to this ledger, so that everyone on the network can have a consistent view of the 'state' of all transactions and balances.
To facilitate this, miners – individuals or entities with high computational power – take a bunch of these transactions, validate them, and group them into a 'block'. This block is then added to the 'chain' of previous blocks, hence the term 'blockchain'.
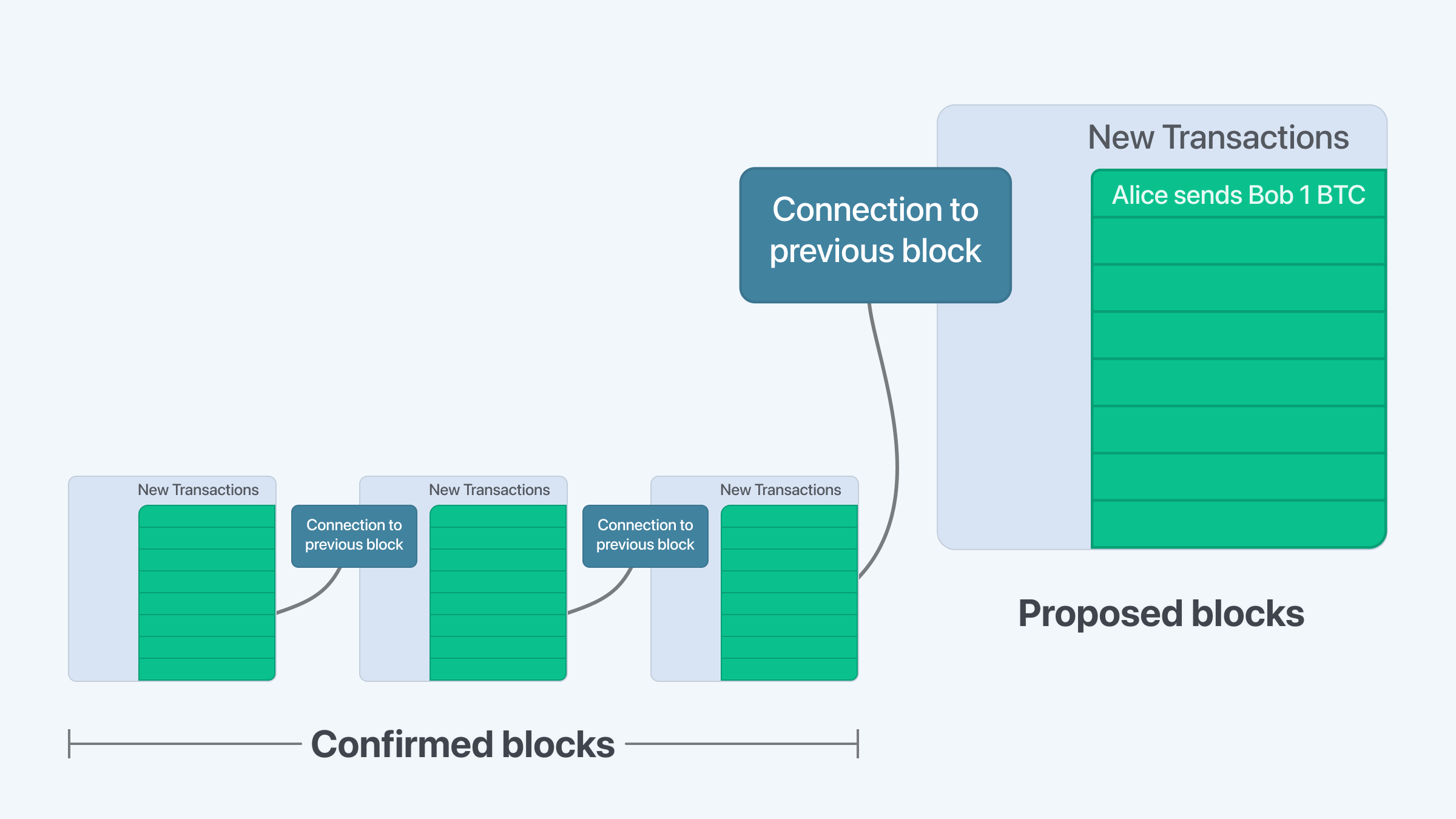
What is a Confirmation?
A confirmation represents the acceptance of a new block (containing several transactions) by the blockchain network. Once a miner has successfully added a new block to the blockchain, one 'confirmation' has occurred. This means that the transactions within the block are verified and are now part of the blockchain.
With each subsequent block that is added to the chain, an additional confirmation is achieved for the blocks before it. For instance, if three more blocks have been added after the block that contains your transaction, your transaction has received four confirmations.
Why Are Confirmations Important?
Confirmations are crucial for maintaining the security and integrity of the blockchain. They prevent 'double-spending', where someone tries to send the same cryptocurrency coins to two different recipients. The more confirmations a transaction has, the more secure it is.
Different cryptocurrencies require different numbers of confirmations before a transaction is considered final. For example, a Bitcoin transaction is often considered secure after six confirmations, while Ethereum transactions are usually considered secure after around 30 confirmations.
Waiting for Confirmations
It's important to note that because each block takes time to be mined and added to the blockchain, there's often a delay between when a transaction is made and when it receives its first confirmation. This waiting period can vary based on the congestion of the network and the transaction fee set by the sender. Transactions with higher fees are typically processed quicker by miners because they provide a higher reward.
Confirmations and businesses
When you're dealing with businesses such as cryptocurrency exchanges, confirmations are especially important. Most businesses require a certain number of confirmations before they consider a transaction complete. This is to ensure the safety of the funds and to prevent potential fraudulent activity. Therefore, when you transact with a business using cryptocurrency, you may have to wait for a while until the required number of confirmations is reached.
Related guides
Start from here →
What are cryptocurrency network fees?
Learn what crypto network fees are, how fees are determined, and more.

What are cryptocurrency network fees?
Learn what crypto network fees are, how fees are determined, and more.

What are Bitcoin network fees?
Discover what bitcoin fees are, how fees are determined, and more.

What are Bitcoin network fees?
Discover what bitcoin fees are, how fees are determined, and more.
What is ETH gas and how do fees work in Ethereum?
Learn about the unit for measuring transaction fees in Ethereum, get details on the Ethereum fee market, and discover how to customize the fees you pay.

What is ETH gas and how do fees work in Ethereum?
Learn about the unit for measuring transaction fees in Ethereum, get details on the Ethereum fee market, and discover how to customize the fees you pay.

What is EIP 1559?
Understand how EIP 1559 overhauled the fee market in Ethereum and what it means for ETH's circulating supply.

What is EIP 1559?
Understand how EIP 1559 overhauled the fee market in Ethereum and what it means for ETH's circulating supply.

What is a token sale?
Token sales are an important part of the crypto ecosystem. Learn their ins and outs.

What is a token sale?
Token sales are an important part of the crypto ecosystem. Learn their ins and outs.

What is an airdrop?
Airdrops are very popular in crypto. Find out what airdrops are, why they are used, and some well known examples.

What is an airdrop?
Airdrops are very popular in crypto. Find out what airdrops are, why they are used, and some well known examples.
What is liquidity?
Liquidity has several slightly different but interrelated meanings. For the purposes of crypto, liquidity most often refers to financial liquidity and market liquidity.

What is liquidity?
Liquidity has several slightly different but interrelated meanings. For the purposes of crypto, liquidity most often refers to financial liquidity and market liquidity.

What are liquidity pools?
A liquidity pool is a collection of cryptoassets that help facilitate more efficient financial transactions such as swapping, lending, and earning yield.

What are liquidity pools?
A liquidity pool is a collection of cryptoassets that help facilitate more efficient financial transactions such as swapping, lending, and earning yield.
STAY AHEAD IN CRYPTO
Stay ahead in crypto with our weekly newsletter delivering the insights that matter most
Weekly crypto news, curated for you
Actionable insights and educational tips
Updates on products fueling economic freedom
No spam. Unsubscribe anytime.



Start investing safely with the Bitcoin.com Wallet
Over wallets created so far
Everything you need to buy, sell, trade, and invest your Bitcoin and cryptocurrency securely

© 2026 Saint Bitts LLC Bitcoin.com. All rights reserved



