DeFi use cases
Last updated

Table of Contents
Asset Management
In its most basic sense, asset management refers to how a person holds and invests their assets. In traditional finance, asset management is most often used to describe third parties who manage assets on behalf of others. Crypto asset management includes both personal holdings, as well as third parties holding and investing on your behalf.
With crypto asset management you can "be your own bank." While this is technically possible in legacy finance, you can keep your fiat money and precious metals under your bed or in a safe, in practical terms you cannot. First, it’s not very safe. Second, you lose access to most financial services and products such as electronic payments, stock trading, and borrowing and lending.
This is not true in crypto. You can retain full control of your assets without giving up any of the conveniences or financial services and products. Self-custodial wallets like the Bitcoin.com Wallet make it easy and safe. You aren’t forced to self custody your cryptoassets if you don’t want to, but the fact that there is always the option means that intermediaries won’t have the unfair gatekeeping advantage that they enjoy in legacy markets.
Read more: What is crypto asset management?
DEX
Decentralized exchanges, or DEXs, are decentralized versions of centralized exchanges (CEXs). Exchanges are a fundamental product for any financial market. They offer a way for buyers and sellers to come together and form a market to trade between assets.
In many ways CEXs are perfect examples of the problem of intermediaries. They’re powerful gatekeepers, deciding which assets can be traded, when they can be traded, and who can trade. This gives them incredible power to influence outcomes for assets, buyers, and sellers. In traditional markets, CEXs are not a single intermediary, but rather composed of up to five or more intermediaries (mobile app, PFOF, stock clearing, dollar clearing, dark pool, exchange, etc…). Each intermediary extracts value from the buyer and seller.
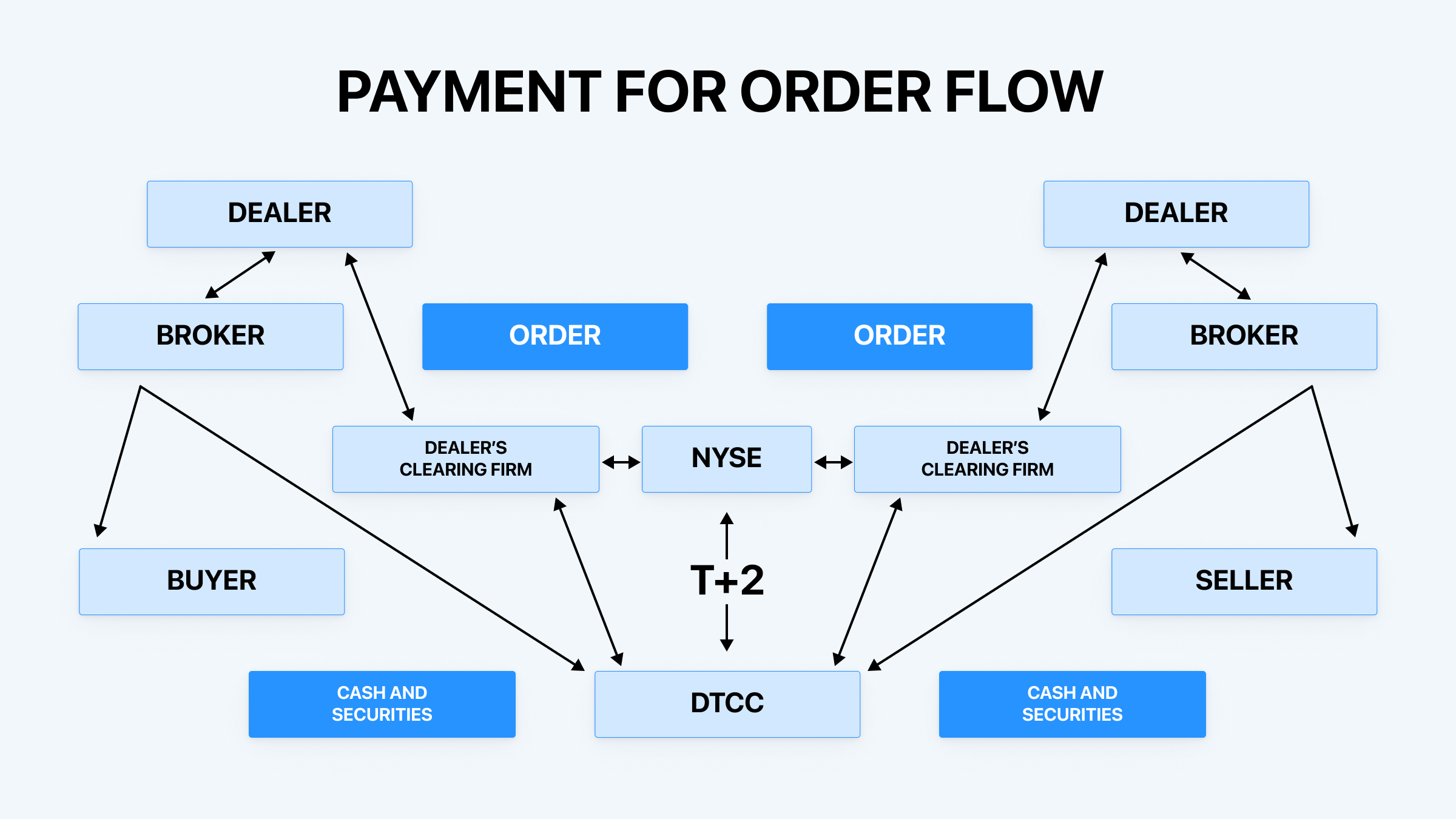 As you can see, PFOF consists of a complicated web of intermediaries on both sides of any transaction, all of whom must be compensated.
As you can see, PFOF consists of a complicated web of intermediaries on both sides of any transaction, all of whom must be compensated.
DEXs can winnow down the number of intermediaries to one – the DEX itself. Importantly, the DEX is an impartial intermediary; a program defined by smart contracts visible to all on the blockchain. DEXs allow anyone to make a market - tradeable anytime, by anyone anywhere in the world. This radical leveling of the playing field strips away many of the entrenched advantages CEX-insiders enjoy.
Currently DEXs are used almost exclusively to trade between digital native assets like Bitcoin (via Wrapped Bitcoin) or Ethereum, but as the world becomes increasingly tokenized, DEXs will be able to facilitate the trade between almost anything – stocks, real estate, commodities, and more.
Read more: What is a DEX?
Lending
DeFi lending allows people to borrow funds from a pool of lenders. The lenders receive yield from the interest borrowers pay. Decentralized lending and borrowing opens up this activity, which is mostly available from financial institutions such as banks in developed countries, to people all over the world, especially in developing countries.
DeFi lending and borrowing innovates on problems in legacy finance. It offers more efficiency, access, and transparency. DeFi lending and borrowing platforms allow anyone anywhere in the world with internet access, the ability to lend and borrow. DeFi loan amounts can be far more granular than even microfinance loans, which have minimums of US$50 to $100. DeFi protocols have significantly lower minimum fees than their legacy finance counterparts, which is particularly important when the loan amount is relatively small. DeFi lending is a very large improvement for developing countries, since it simply isn’t available unless you have bank access and a minimum amount of money to lend. Finally, retaining full custody of your funds reduces the risk practically to zero that the third party holding your funds will mismanage your assets.
Read more: What is crypto lending?
DAOs
DAO stands for Decentralized Autonomous Organization. DAOs are a new way to structure organizations online where the rules are embedded in and executed by smart contracts. Other than that, DAOs can take the hierarchy of any other organization, whether that be completely flat with no central leadership, or highly stratified like you see in a typical large company.
A reasonably analogous way to think of a DAO is as a company. Companies are composed of people who follow rules. Those rules are ultimately enforced by the laws of the companies’ jurisdiction. DAO rules are enforced not by law, but by code in smart contracts.
DAOs bring the benefits of crypto to organizational structures: trustless, transparent, composable, decentralized.
In the increasingly internet-based world, DAOs can be a more efficient way to create organizations, especially organizations spread across the world and with large treasuries. There have been plenty of successful internet-based organizations, but once money, especially large sums of money is involved, those organizations rarely can remain internet first. They incorporate somewhere.
Read more: What is a DAO?
Derivatives
A crypto derivative, such as a “perpetual futures," is a financial instrument that “derives" its value from an underlying cryptocurrency or digital asset. For example, there are many perpetual futures contracts based on Bitcoin. Derivatives are contracts between two or more parties. The most common type of derivatives in crypto markets are the aforementioned perpetual futures, with traditional futures and options a distant second and third.
In crypto’s short history, the most popular place to trade derivatives has been on centralized exchanges. These exchanges provided liquidity and a responsive trading environment, both of which are important for shorter time frame derivatives trading. A major drawback has been many allegations that centralized exchanges have abused their privileged place of information to actively trade against their customers. Also, during major market events, centralized exchanges have been apt to go offline, causing customers with open positions to be liquidated.
This is slowly changing as DeFi matures. Now there are a handful of viable decentralized derivatives platforms. They still lack the liquidity depth and responsiveness of centralized exchanges, but those differences will likely narrow over time.
Read more: What are crypto derivatives?
Prediction markets
Prediction markets are marketplaces where people trade on the outcomes of future events. Market prices can indicate what the marketplace believes the probability of the event is. Most prediction markets are a binary option market (e.g., “yes" or “no), where the two options will expire at the price of 0% or 100%. Before expiry, the two assets trade between 0% and 100%, which indicates what the marketplace thinks the odds are. Prediction markets have proven to be relatively active at predicting future events.
There are many centralized prediction markets regulated by traditional financial institutions like the SEC. The most important problems with these centralized markets is that they have low limits on how much each person can bet and high fees (e.g., a 5% withdrawal fee on PredictIt). The first problem limits the predictive power of prediction markets, because even if a person has very strong conviction about an outcome and the means to back it up, they are capped at limits well under $1,000. The second problem is endemic throughout traditional finance, but is absent in DeFi.
Read more: What are prediction markets?
Stablecoins
Stablecoins aren’t an exclusive use case of DeFi, but the two have been highly synergistic. Stablecoins make DeFi more usable, and in turn DeFi increases the volume of use of stablecoins. Stablecoins are a kind of tokenized version of fiat currency. Most stablecoins are tokenized digital dollars. Stablecoins have become the most popular trading pair for cryptoassets because they give people price stability in crypto, which is a very volatile new asset class. On DEXs or lending and borrowing protocols, stablecoins are the most used cryptoasset.
In parts of the world, stablecoins are starting to be used for everyday commerce. For example, in Southeast Asia, USDT is used for P2P payments and is even accepted at 7-Eleven in some areas. Stablecoins are being used for cross-border payments, especially in countries starved for US dollars; an understandable development since US dollars account for approximately 70% of world trade.
Investors and businesses are not the only ones who have realized the value of stablecoins. Governments around the world have implicitly recognized the fundamental use case of stablecoins by en masse committing to Central Bank Digital Currencies (CDBC), which are essentially nation-state backed stablecoins.
Read more: What are stablecoins?
Metaverse
The metaverse is the next stage in the evolution of the internet. The metaverse is the internet mediated by graphically rich 3D spaces with an increasing focus on virtual and augmented reality.
Crypto introduced the idea of digital scarcity, which enables digital ownership. Many components of crypto will play pivotal parts in the metaverse. DeFi primitives, like those on this list of use cases, will be building blocks that the metaverse needs to function.
The metaverse is hard to describe as just one thing, much like the internet. Check out the article below for a better understanding of what the metaverse is, and its potential.
Read more: What is the metaverse?
Insurance
Insurance is necessary for a successful economy. Globally, it generated US$5.8 trillion in premiums in 2020. Yet much of the process is labor intensive, paper-based, and redundant. Insurance companies also have a sprawling coordination problem.
Many traditional and crypto companies are exploring how to use blockchain to tackle the inefficiencies in insurance. For example, legacy insurance companies such as State Farm and USAA already use a blockchain-based system. Anthem, the second largest health insurance company in the US, has started to use blockchain to securely access and share their medical data.
Crypto-native companies like Nexus Mutual are creating decentralized insurance on the blockchain for crypto projects, such as smart contract insurance and DEX insurance. As DeFi grows, the need for decentralized insurance will grow at a commiserate rate. Other DeFi insurance companies are beginning to move into legacy insurance markets, such as flight delay insurance. With the efficiencies that come from DeFi, there is real potential to disrupt the multi-trillion dollar insurance market.
Identity
Once your identity is on the blockchain, people gain access to many more efficient services. This includes banking, real estate, and government services. Governments reap the benefits of more efficient services too. McKinsey indicates that, “improving customer registration could reduce onboarding costs by up to 90 percent, and reducing payroll fraud could save up to $1.6 trillion globally." High quality identification is important for ensuring access to a large number of foundational services. From healthcare to financial services to education.
Conclusion
Though DeFi is advancing quickly, it has still only begun to touch the surface of what’s possible. In the coming years, it is likely that new DeFi use cases will emerge that were not possible in the legacy system.
Ready to start your DeFi journey? Get the multichain Bitcoin.com Wallet where you can connect to DApps that enable DeFi uses.
Related guides
Start from here →
What is DeFi?
Learn what makes decentralized finance (DeFi) apps work and how they compare to traditional financial products.

What is DeFi?
Learn what makes decentralized finance (DeFi) apps work and how they compare to traditional financial products.

What is a DEX?
A decentralized exchange (DEX) is a type of exchange that specializes in peer-to-peer transactions of cryptocurrencies and digital assets. Unlike centralized exchanges (CEXs), DEXs do not require a trusted third party, or intermediary, to facilitate the exchange of cryptoassets.

What is a DEX?
A decentralized exchange (DEX) is a type of exchange that specializes in peer-to-peer transactions of cryptocurrencies and digital assets. Unlike centralized exchanges (CEXs), DEXs do not require a trusted third party, or intermediary, to facilitate the exchange of cryptoassets.

What are ERC-20 tokens?
Learn the basics of the Ethereum token standard, what ERC-20 tokens are used for, and how they work.

What are ERC-20 tokens?
Learn the basics of the Ethereum token standard, what ERC-20 tokens are used for, and how they work.

What's a smart contract?
Get the basics on the "software" that runs on decentralized networks.

What's a smart contract?
Get the basics on the "software" that runs on decentralized networks.

What are stablecoins?
Learn about the key US-dollar crypto 'stablecoins,' how they remain stable, what they're used for, ways to earn interest on them, and where to get them.

What are stablecoins?
Learn about the key US-dollar crypto 'stablecoins,' how they remain stable, what they're used for, ways to earn interest on them, and where to get them.

What are NFTs?
Learn about NFTs, how they work, examples of prominent NFTs, and much more.

What are NFTs?
Learn about NFTs, how they work, examples of prominent NFTs, and much more.
STAY AHEAD IN CRYPTO
Stay ahead in crypto with our weekly newsletter delivering the insights that matter most
Weekly crypto news, curated for you
Actionable insights and educational tips
Updates on products fueling economic freedom
No spam. Unsubscribe anytime.



Start investing safely with the Bitcoin.com Wallet
Over wallets created so far
Everything you need to buy, sell, trade, and invest your Bitcoin and cryptocurrency securely

© 2026 Saint Bitts LLC Bitcoin.com. All rights reserved




